Where is South China Sea? What countries are in the South China Sea
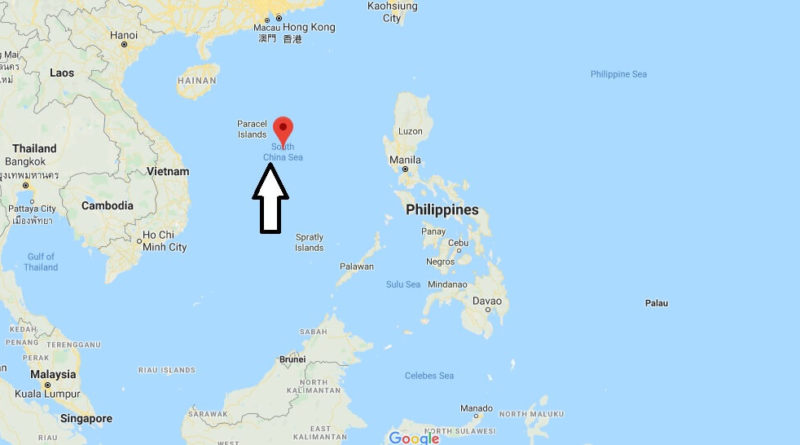
Where is South China Sea?
The South China Sea (Chinese: chinesisch nán Hii ‘southern sea’, Vietnamese: Binn đông, “eastern sea”) is a part of the Chinese sea and marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean in Asia, which includes the Gulf of Thailand and the Gulf of Tonkin.
The South China Sea covers an area of 3,685,000 km2. At an average depth of 1,060 meters, this results in a water volume of 3,907,000 km3. The greatest depth is 5,016 metres in the China Sea Basin.
It is located between China, the Indochinese and the Malay Peninsula as well as the islands of Taiwan, Luzon, Palawan and Borneo. Neighbouring countries are the people’s Republic of China, Republic of China (Taiwan), Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam.
The South China sea, is separated in the North-East by Taiwan, the East China sea, to the South by the Philippine island of Palawan from the Sulu sea, in the East on the 320-km-wide Luzon Strait of the Philippine sea and the South through the Karimata street, with the Java sea is connected. In the southwest, the Strait of Malacca connects.
Does South China Sea belong to China?
Where is the South China Sea located in relation to China?
What is the significance of the South China Sea?
What does China claim in the South China Sea?
What countries does China control?
Is Taiwan a part of China?
Is South China Sea the largest sea in the world?
Who owns the Spratly Islands?